#Research Australia
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Video
DSC05570 orig with insert tag by Jim Via Flickr: Visual sighting from my property in Greta, NSW Australia taken on NV setting. This is a unedited version of the NV capture of the multiple craft. With the cropped enhanced insert for a closer inspection of the craft... Dimensional Entities. FRJS Research Australia
#Dimensional Entities#anomalies#Antigrav#Australia#craft#Disclosure#entities#My Sky#Night sky#phenomena#Research#Science#sky#sky anomalies#Sony HDR-SR12E#Truth#ufo#UFOs#unknown#Australian Research#FRJS Australia Research#FRJS Research Australia#FRJS Research discovery 2009#my research#Research Australia#Research of UAP's#scientific research#Scientific research Australia#UFO Researchers#Australian Discoveries 2009
0 notes
Text
Gerstner Postdoctoral Fellow Daniel Hooper (@danielmhooper) studies the genetics of color evolution in Australian finches at the Museum. He recently published a study on the genetics of color variation in Long-tailed Finches and shares his findings on why some of these finches have red beaks, while others have yellow or orange beaks. This research, recently published in Current Biology, was all catch and release.
Fieldwork photos courtesy of Daniel Hooper, Geoffrey Giller, and Simon Griffith.
#science#amnh#museum#nature#natural history#animals#did you know#fact of the day#birds#ornithology#australia#long tailed finch#research#stem#genomics#biology#museum of natural history#american museum of natural history
317 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Australian Gooberment is at it again…trying to eliminate freedom of speech and take down anyone who opposes their oppressive regime 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourselves#reeducate yourself#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your own research#do some research#do your research#ask yourself questions#question everything#australia#government corruption#evil lives here#new world order#news#censorship
313 notes
·
View notes
Text
Australia's b girl Raygun may have lied on her resume, but she got a trip to Paris, free gear, access to the Olympic chocolate muffins, and is forever an Olympian, PhD brain outsmarted 😭
#i knew as soon as i saw that first throw down they were gonna cook her on the internet#rachel gunn#raygun#breakdancing#olympics#paris 2024#team australia#paris olympics#she used the phd brain to the fullest#kmow she needed some research for that thesis lmfao
297 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Since 2019 I have endured six workplace investigations because of my advocacy and research on abortion and in every investigation I have been cleared of misconduct,”
Howe stated that she had endured six separate workplace investigations since 2019 regarding her pro-life research. She was found innocent of misconduct in each case, including the most recent investigation launched at the beginning of the year, which determined she was innocent of any breach in the Australian Code for Responsible Research.
Seems universities really don’t like when you conduct research on abortion if it’s not going to swing in favor of the pro-abortion stance.
#that’s at least what I’m getting from this#abortion#prolife#pro life#pro-life#Australia#abortion research#religion mention
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Love how everyone was so worried and worked up over KOSA but then when australia says "face id is required to prove your over 16 to use social media" noone even hears about it
#disclaimer: I don't know the full story#i don't wanna research it for the sale of my mental health#disclaimer 2: yes I am using this blog purely because of it's popularity and amount of followers so this kind of thing gets heard#auspol#stop kosa#kosa#australia#ausgov#do not take my word for straight fact there's more to the story and you should do your own research but this has been a developing thing#for a while
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
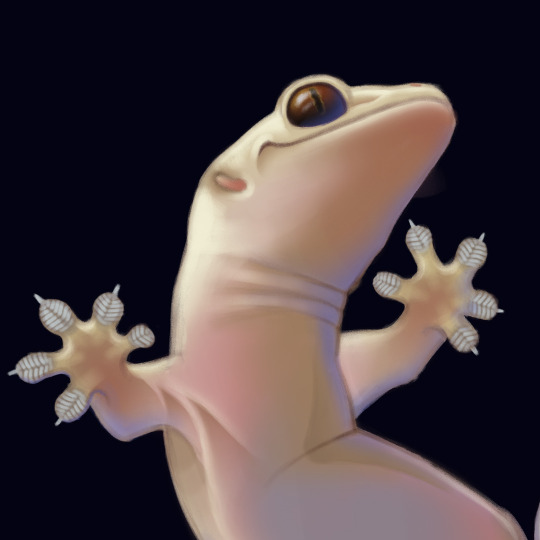
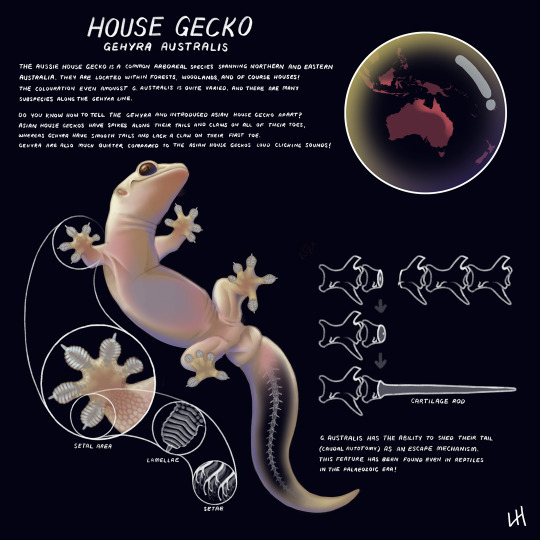

Bringing back the little infographics again 🦎
We always hear little chirping noises coming from the roof, but we rarely get to see which type(s) of geckos we have hiding up there....
I started thinking more about them and their features so I thought I'd share my findings 😊 Enjoy!
インフォグラフィックを戻ってきた 🦎 毎日屋根のなかに小さくさえずるを聞こえるけど、なにもみえない。どんなヤモリがいますか?
いつもかんがえる。そして、このインフォグラフィックがある。お楽しみください!
Relevant links to interesting papers here: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Simplified-three-dimensional-model-provides-in-as-Amorim-Travnik/856e592b3cf45a98be2b67a0927c51a399a406e7/ https://nyuad.nyu.edu/content/dam/nyuad/academics/divisions/engineering/lizard-tail/bioinspired-lizard-robot.pdf https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-21526-3
#2D#art#アート#芸#illustration#gecko#australia#housegecko#ヤモリ#reptilesofinstagram#爬虫類#infographic#science#科学#research#herpetology
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Five people have gone into remission thanks to advancements in medicine — and a sixth patient may also now be free of HIV.
One of the biggest breakthroughs in HIV/AIDS prevention in recent years is the widespread use of PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis).
This drug therapy, approved by the Federal Drug Administration in 2012, has been a key player in preventing HIV transmission through sex or injection drug use. Antiretroviral drugs, such as PrEP, also slow the replication of the virus and prevent it from progressing to AIDS.
Although PrEP has become a more accessible treatment for the virus, scientists have been hurriedly working towards cures for HIV for decades — and we’re finally seeing some results.
In February of this year, scientists in Germany confirmed a fifth-ever patient had been cured of HIV after receiving stem cell transplants that include genetic mutations that carry a resistance to HIV.
But it looks like a sixth patient may soon be able to join this very exclusive club.
The man, referred to as the “Geneva patient,” underwent a stem cell transplant after cancer treatment, though these cells did not include the HIV-resistant genetic mutation.
Still, he went off antiretroviral therapy for HIV in November 2021, and his viral load remains undetectable.
Instead, doctors are researching whether a drug called ruxolitinib may be partially responsible for his recovery.
Ruxolitinib decreases inflammation associated with HIV by blocking two proteins, JAK1 and JAK2. This helps kill off “reservoir cells” that lay dormant in the body and have a potential to cause rebounds in patients with HIV.
Experts say the AIDS crisis can end by 2030 across the globe — as long as leaders prioritize this goal.
A new report from UNAIDS shows a clear, optimistic path to ending the AIDS crisis. (This looks like a 90% reduction in cases by 2030.)
The organization’s report includes data and case studies that show that ending AIDS is a political and financial choice — and that governments that have prioritized a path towards progress are seeing extraordinary results.
By following the data, science, and evidence; tackling inequality; and ensuring sufficient and sustainable funding across communities, the global community could wipe out the AIDS pandemic by the end of the decade.
The report demonstrates that progress has been strongest in the countries and regions that have the most financial investments, like eastern and southern Africa, where new HIV infections have been reduced by 57% since 2010.
Investments in treatments, education, and access to care have also led to a 58% reduction in new HIV infections among children from 2010 to 2022 — the lowest number since the 1980’s.
Plus, the number of people on antiretroviral treatment around the globe has risen from 7.7 million in 2010 to 29.8 million in 2022.
The moral of the story? This goal can be achieved, if world leaders put their minds — and wallets — to it.
A region in Australia might be the first place in the world to reach the United Nations targets for ending HIV transmission.
Researchers believe that the central district of Sydney, Australia is close to becoming the first locality in the world to reach the UN’s target for ending transmission of HIV.
Specifically, new infections among gay men have fallen by 88% between 2010 and 2022. In fact, there were only 11 new HIV cases recorded in central Sydney last year, and almost all HIV-positive Australians are on antiretroviral drugs.
... "These numbers show us that virtual elimination of HIV transmissions is possible. Now, we need to look closely at what has worked in Sydney, and adapt it for other cities and regions across Australia.”
Namibia is ahead of schedule in UN targets to end HIV/AIDS.
Although the virus is still the leading cause of death in Namibia, the country is well on track to hit 95-95-95 UNAIDS targets before its 2030 deadline.
In Namibia, 92% of people know their HIV status, 99% of people living with HIV are on treatment, and 94% of people living with HIV who are on treatment are virally suppressed.
In addition to these exciting statistics, new infections have plummeted. The estimated rate of new HIV infections in Namibia is five times lower than it was in 2002, according to the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention.
These encouraging numbers are thanks to the investment and strategic response of PEPFAR, but also to the willingness of local governmental agencies and organizations to adhere to the UN’s Fast-Track approach.
Breakthroughs are being made in HIV vaccine therapies.
Long before we were all asking each other “Pfizer or Moderna?” about our COVID-19 vaccines, scientists have been researching the potential of mRNA vaccines in treating some of the world’s deadliest diseases — like HIV.
And with the success of our mainstream mRNA vaccines, an HIV inoculation remains a goal for researchers across the globe.
Last year, the National Institutes of Health launched a clinical trial of three mRNA vaccines for HIV, and similar studies are being conducted in Rwanda and South Africa, as well.
CAR T-cell clinical trials are underway to potentially cure HIV.
This spring, UC Davis Health researchers have dosed the second participant in their clinical trial, which poses the use of CAR T-cell therapy as a potential cure for HIV.
The study involves taking a participant’s own white blood cells (called T-cells), and modifying them so they can identify and target HIV cells, ultimately controlling the virus without medication.
The first participant in the study was dosed with anti-HIV T-cells last August, and the trial is the first of its kind to utilize this technology to potentially treat HIV.
Of course, the trials have a long way to go, and the lab is still preparing to dose a third participant for the study, but CAR T-cell treatments have been successful for lupus and forms of cancer in the past...
“So far, there have been no adverse events observed that were related to the treatment, and the two participants are doing fine.”
Guidance on how to reduce stigma and discrimination due to HIV/AIDS is reaching people around the globe.
While the stigma surrounding HIV and AIDS has significantly decreased — especially towards the LGBTQ+ community — with advancements in treatment and prevention, discrimination is certainly not gone.
While most people now understand HIV/AIDS better than they did decades ago, those most impacted by the virus (like gay men and low-income women and children) still face ongoing barriers to care and economic security.
It is vital to maintain awareness and education interventions.
After all, experts suggest that eliminating discrimination and stigma are key factors in reducing disease. And not eliminating stigma impedes HIV services, argues UNAIDS, “limiting access to and acceptance of prevention services, engagement in care, and adherence to antiretroviral therapy.”
Luckily, UNAIDS provides guidance on how to reduce stigma and discrimination in the community, workplace, education, health care, justice, and emergency settings.
The goal is to, of course, decrease stigma in order to decrease disease, but also to provide folks with the culturally significant support they need to live safe, integrated lives — with or without disease.
For instance, a 2022 study conducted in Northern Uganda showed that local cultural knowledge passed through Elders was a successful intervention in reducing HIV-related stigma among young people.
“Research in school settings has shown that the use of local cultural stories, songs, myths, riddles, and proverbs increases resilient coping responses among students and strengthens positive and socially accepted morals and values,” the study’s discussion reads.
So, while an uptick in acceptance gives us hope, it also gives us a directive: Keep telling the accurate, full, and human stories behind HIV/AIDS, and we’ll all be better for it. "
-via GoodGoodGood, August 3, 2023
#hiv#hiv/aids#aids crisis#public health#medical research#vaccines#australia#namibia#united nations#queer issues#trans issues#lgbtq issues#lgbtq community#infection prevention#good news#hope
275 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tbh one of the reasons I haven't gotten around to Palmarosa yet is because I knew I had to do a fuckton more worldbuilding research and couldn't be bothered because I was like 'this is going to be a lot more work than it needs to be.'
And after 4 straight hours and over 50 tabs which distilled down into 2000 words of worldbuilding that isn't even me getting to the chapter yet, I was right lmao. But in good news, it means I can officially get started! We're going to Luskan, folks :D
#palmarosa#thespectaclesofthor#i've got a bunch of new characters whose names we'll probably never learn#even though they have names#and i've researched more into espruar than i ever cared to#and then had to invent some new terms#anyway i tried to keep the worldbuilding as short as possible#i could write *two chapters* in four hours with the right motivation#so sometimes i get a little annoyed at how long worldbuilding takes#when most of it never ends up in the story lmao#sdalkjfsdlakfjas#i also found a line of scandinavian perfumes i kind of want to try#only to find out they don't ship to australia so
54 notes
·
View notes
Video
20090703060539(78)rsz tag by Jim Via Flickr: Visual sighting from my property in Greta, NSW Australia taken on NV setting. This is a edited version of the NV capture of the craft. FRJS Research Australia
#Dimensional Entities#Disclosure#Dimension#UFOs#UAP dimensional craft#Research Dimensional Entities truth Disclosure Australian UFO sightings Australian UFOs Dimensions Quantum Physics ignorant lost science#Research#Research Australia#Australian Research#Australia#Australian Night Sky#Australian Sky#craft#Light Entities#Light powered Craft#flickr
0 notes
Text
look, did i set out to write a post season 3 helen x dale fic that would turn into a 15k to 20k giant ass slowburn oneshot?
i did not, but at this point i have fully embraced it

#they are and will never be platonic to me#they have such a beautiful love and deep bond you know they have the best sex come on#anyway this fic is going places#literally. dale is going to three different CONTINENTS in this fic (not counting Australia) i am going insane with the historical research#and the thematic resonance for each of these journeys 💀#and the in betweens#you just get me liveblogging the writing of this whoops i guess#hyperfixating on my own story always a fun time#officially over the 10k line#writing#helen x dale
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Uluru in Australia 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do some research#do your own research#do your research#ask yourself questions#question everything#uluru#australia#travel
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reading this morning Trump funding cuts are now affecting health research teams HERE in AUSTRALIA.
God I am so fucking sick of America, sorry Americans.
#kerytalk#us politics#let me rant okay#I am literally on another continent why do we have to be affected by america's bad decisions#also the news commentary on the us is fucking constant i am so goddamn tired#I DON'T EVEN LIVE IN THE US#anyway this is why I'm glad mandatory voting in Australia is a thing cause hooooo boy#i may also be extra cranky because i have to go do a stress echocardiogram that i don't want to do this morning but I digress#why should we be punished for the poor research and propaganda recognition failure of another country#also extra pissed that its targeting health research as someone with the chronic unsolved fatigue condition here#might i add one of the interviewed teams being hit are INFECTIOUS DISEASE RESEARCHERS
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
#bungou stray dogs#dogs of tumblr#bungou gay dogs#bungo stray dogs fanart#dogs#dog man#dogblr#dog#science#pro science#the glass scientists#mad scientist#data scientist#research scientist#scientist#class war#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#anti apple#anti capitalism#antifascist#antifaschistische aktion
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
An early example of a reply guy, writing directly to the king to complain about the "disloyalty of many prominent persons within the Commonwealth of Australia, especially in New South Wales."

their speeches argue for a "republican government of Australia and in which the Crown is spoken of with the utmost hatred" sounds pretty fucking cool to me
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

Scientists have discovered that bacteria transferred during intercourse, known as the genital microbiome or "sexome," leave unique signatures that can help identify sexual assault perpetrators, even in cases where DNA evidence is absent. A study by Australian researchers found that these bacterial signatures, detectable through a gene called 16S rRNA, persist even when barrier protection like condoms is used.
The findings could revolutionize forensic investigations, particularly in cases with no sperm detection, offering a new tool to bring perpetrators to justice. This breakthrough highlights the potential of microbiome analysis in solving crimes and supporting survivors.
#general knowledge#affairsmastery#generalknowledge#current events#current news#upscaspirants#upsc#generalknowledgeindia#world news#news#research#technology#biology#biological#science news#science#scientists#dna#crime and punishment#exploitation#investigation#australia#men sperm#rna#justice#freedom#analysis#analyst
8 notes
·
View notes

